ENTSTEHUNGSURSACHEN DES VALUE BASED MANAGEMENT
Ansätze zur Bewertung
Die folgenden Methoden beschäftigen sich mit der Festsetzung des Unternehmenswertes.
Equity value represents the value of everything but only to the investors. Whereas the value of a company represents the value of the company´s core business to all investors in the company.
This is why items are added such as unfunded pensions or capital leases or subtracted such as property, working capital and excess cash because they either have to do with the company´s core business activities or not.
Additionally, there is dysmetry of information when evaluating a company. In the management team, in the environment in which the company operates or wants to operate:
Eigenshaften des Mgmt
- Fähigkeiten und Qualifikation des Managements
- Fairness, Entgegenkommen des Managements
- Situationsadaquanz der Managemententscheidungen
- Fleiß, Anstrengung und Sorgfalt des Managements
Umfeldzustände
Some of these items eg. Capital Leases and Unfunded Pension plans are embedded in the financial statements or in the notes. These require time to find and locate.
Ansätze zur Bewertung
Die folgenden Methoden beschäftigen sich mit der Festsetzung des Unternehmenswertes.
Equity value represents the value of everything but only to the investors. Whereas the value of a company represents the value of the company´s core business to all investors in the company.
This is why items are added such as unfunded pensions or capital leases or subtracted such as property, working capital and excess cash because they either have to do with the company´s core business activities or not.
-
Shareholder Value Analyse
Die aus den USA stammende Shareholder Value Analyse beurteilt das Handeln eines Unternehmens wertorientiert aus der Sicht der Shareholder (= Anteilseigner). Der Wert wird dabei aus zukünftigen Zahlungen prognostiziert und soll an sein Maximum gebracht werden.
Shareholder Value = Barwert Free Cash Flows
+ Operatives Ergebnis vor Steuern und Zinsen (1)
- adaptierte Steuern auf das EBIT (2)
= Operatives Ergebnis vor Zinsen
+ Abschreibungen (3)
+ Erhöhung der Rückstellungen (3)
= operativer Brutto-Cashflow
– Investitionen in Anlagevermögen (4)
- Veränderung des Working Capital (5)
= Operativer Free Cash-Flow
+ Lagerbestände
+ Forderungen aus Lieferung und Leistung
+ Kasse
– kurzfristige Verbindlichkeiten
==================
= Working Capital
-
Stern und Stewart entwarfen in den 1990er Jahren eine Überrendite-Kennzahl. Diese gibt an, ob eine Unternehmung einen Gewinn erzielte, der die Kapitalkosten übersteigt.
EVA = NOPAT – (k x capital)
NOPAT = Net operating profits after tax.
k x capital) is the finance charge
k = the firms weighted average cost of capital
capital = equity plus long-term debt of the company at the start of the period
3. Cashflow Return on Investment
Dieser Bewertungsansatz ermittelt mithilfe des internen Zinsfußes, welche Renditen die Bruttocashflows des Anlagevermögens ergaben.

Brutto Cash Flow - Ökon. Abschreibung
/ Brutto Investitionsbasis > WACC
4. Market-to-Book-Ratio
Das Market-to Book Ratio entspricht der Marktkapitalisierung dividiert durch das Eigenkapital eines Unternehmens. Anders gesagt, ist es das verhältnis von Börsenkurs zu Bilanzkurs.
Barwert Free Cash Flows / Investment > 1
Barwert Free Cash Flows / Investment > 1
Investment = AV(Buchwert) + Working Capital (Buchwert)
Working Capital = UV(Buchwert) - Zinsfreies FK
Bruttoinvestitionsbasis = AV(AK/HK) + Working Capital (AK/HK = BW)
Brutto Cash Flow = Oper. Cash Flor vor. Inv. WC + FK Zinsen (1-S)
Ökonomische Abschreibungen = AV (AK/HK) * q-1 / q^2 - 1
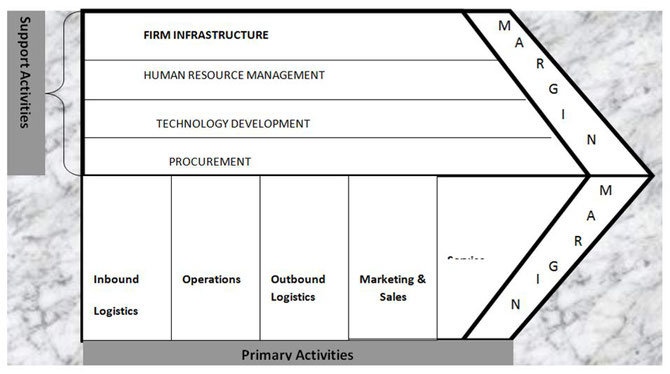
The Generic Value Chain (Source: Porter, 1985)
Strategic capability: Strategic capability is the resources and competences of an organization. These are crucial inseparable parts of every organizational success (Market)
Unique resources: These are the unique resources that are interconnected element of competitive advantage, especially because cannot be duplicated or imitated by competitors. (Shareholder)
Core competencies: Core competencies are activities that are interconnected to competitive advantage and furthermore cannot be duplicated or imitated by competitors. (Resources)
 communication partner
communication partner


